Method
We propose Temporal Score Rescaling (TSR), a simple method that controls the likelihood-diversity trade-off for diffusion and flow models. TSR can be easily applied to any off-the-shelf diffusion or flow model, without any training or extra inference-time computation.
Given a pretrained diffusion model predicting noise $\epsilon_\theta(x,t)$ and parameter $k$ controlling the temperature, during the sampling process, TSR replaces $\epsilon_\theta(x,t)$ with a scaled prediction:
where $\alpha_t$, $\sigma_t$ are the diffusion noise schedule given by $x_t = \alpha_t x_0 + \sigma_t \epsilon$. $\sigma$ is a user-input parameter.
For a flow matching model predicting flow velocity $v_\theta(x,t)$, TSR replaces it with the following velocity:
Steering Distribution with TSR
By controling the inverse temperature $k$, we can steer the sampled distribution to be sharper (larger $k$) or broader (smaller $k$). At $k=1$ TSR yields the original distribution.
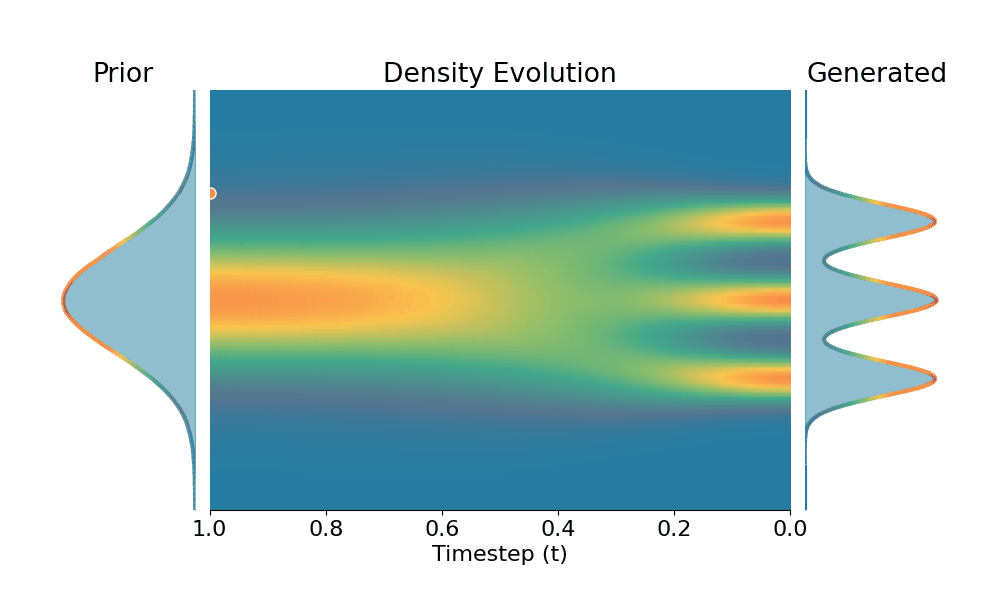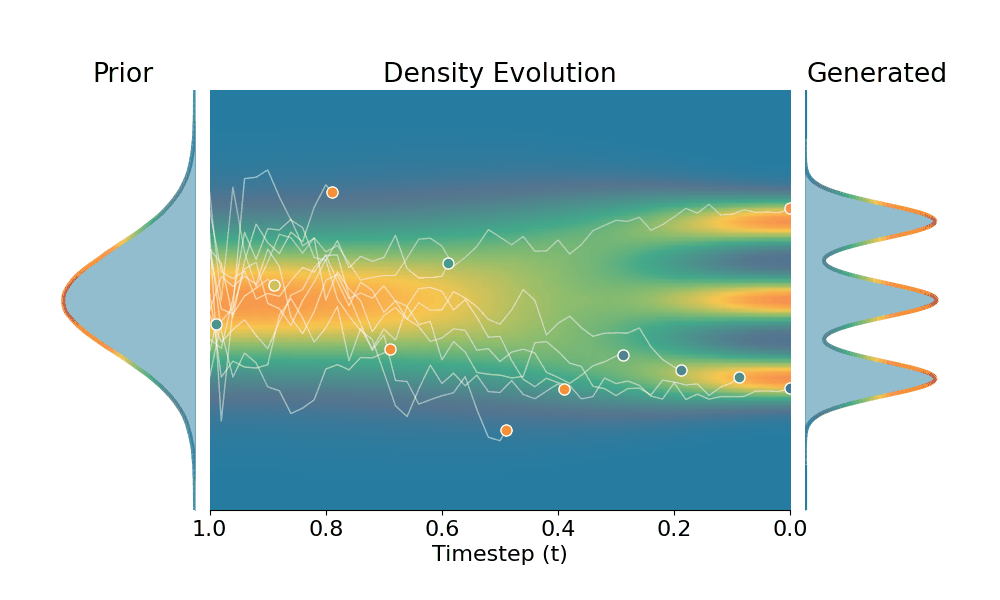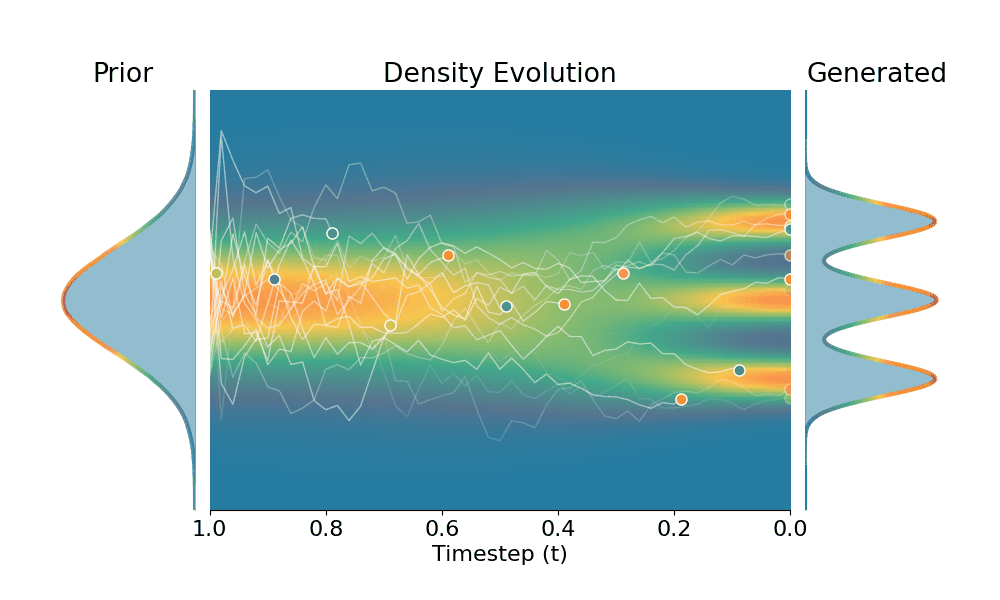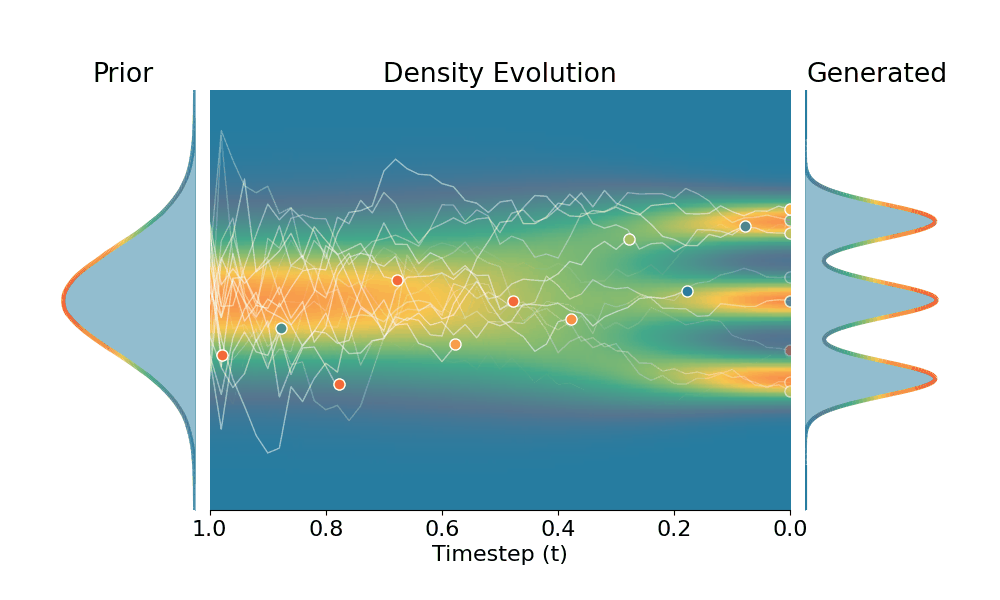
Original (DDPM)
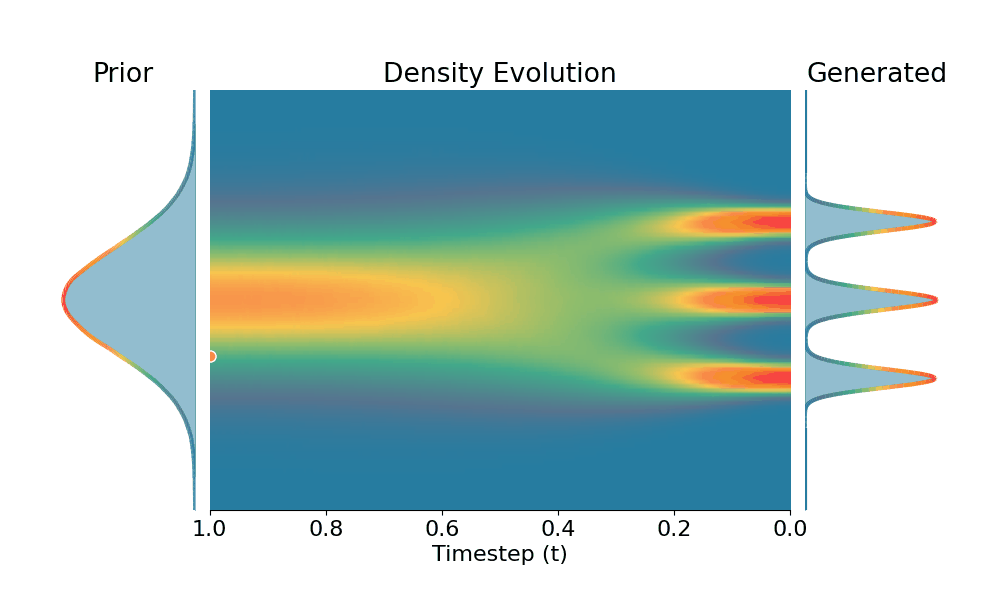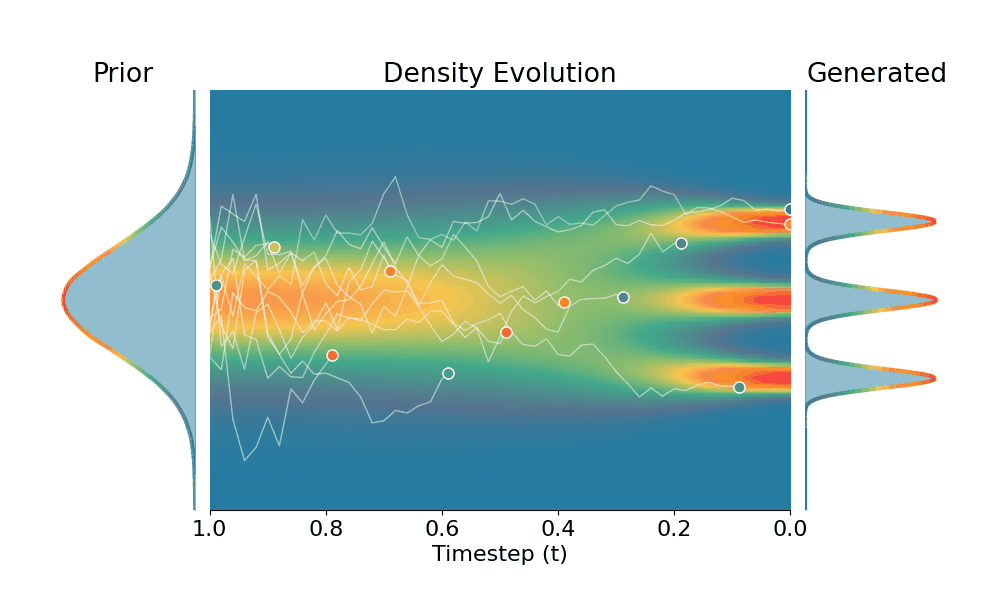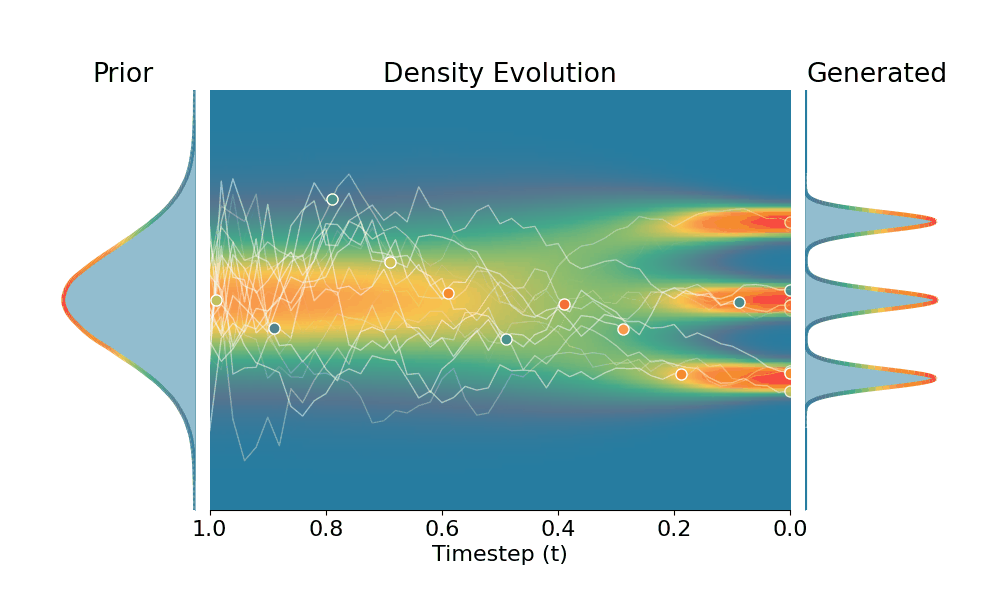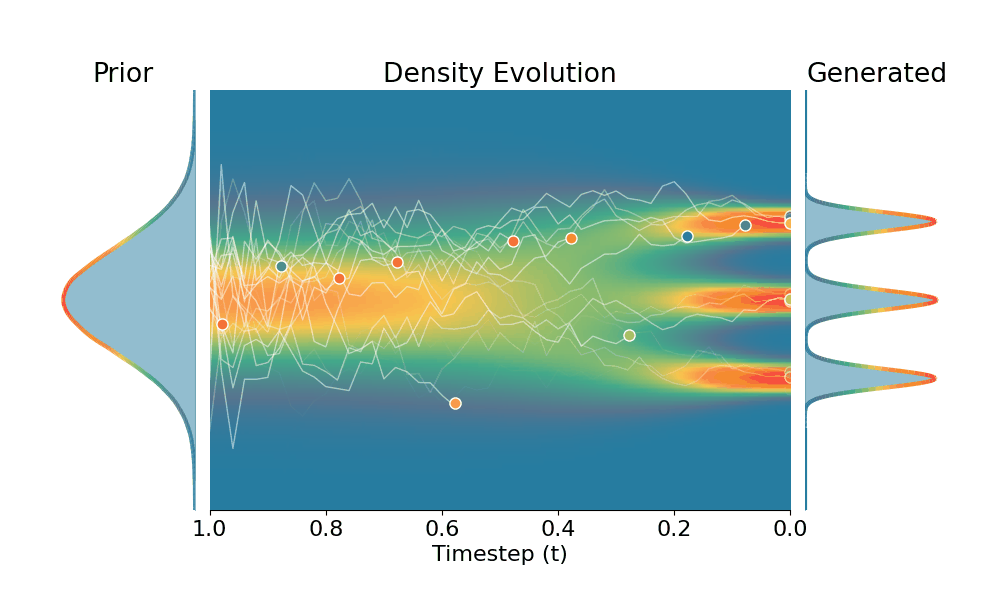
+Temporal Score Rescaling (Ours)
Drag the slider to control the $k$ values. Each plot shows the prior distribution (left), the probability density evolves over time (middle), and the final generated distribution (right). We also show real sample trajectories during the reverse diffusion process.
Comparison with Prior Methods
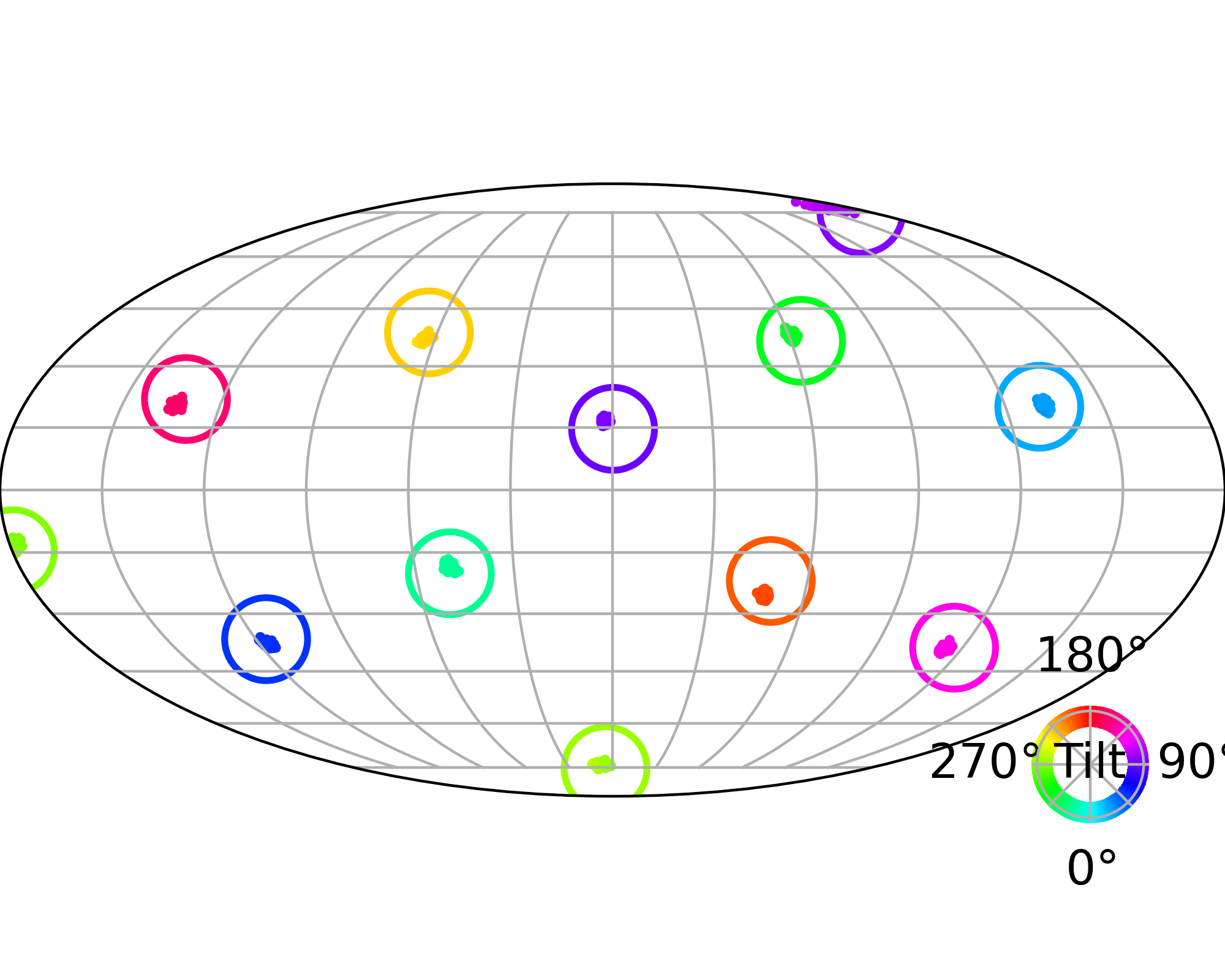
Here we evaluate conditional generation where the data distribution is an isotropic mixture of 6 Gaussians, with the top 3 modes belonging to class 1 and the bottom 3 modes to class 2. We show the sampled conditional distribution for class 1. We compare TSR with Constant Noise Scaling (CNS), the de facto approach for 'pseudo temperature' sampling with diffusion models and Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG). As shown below, both CNS and CFG distort the distribution, while TSR preserves the equal weights between modes. Moreover, CNS does not apply on deterministic samplers (e.g., Flow-ODE), while TSR applies to any diffusion and flow models with any samplers.
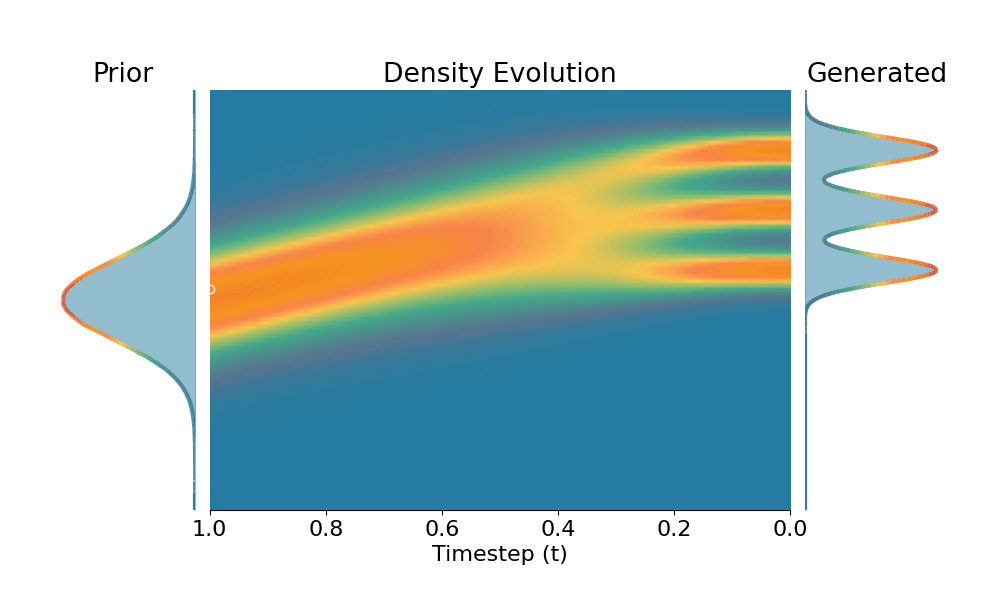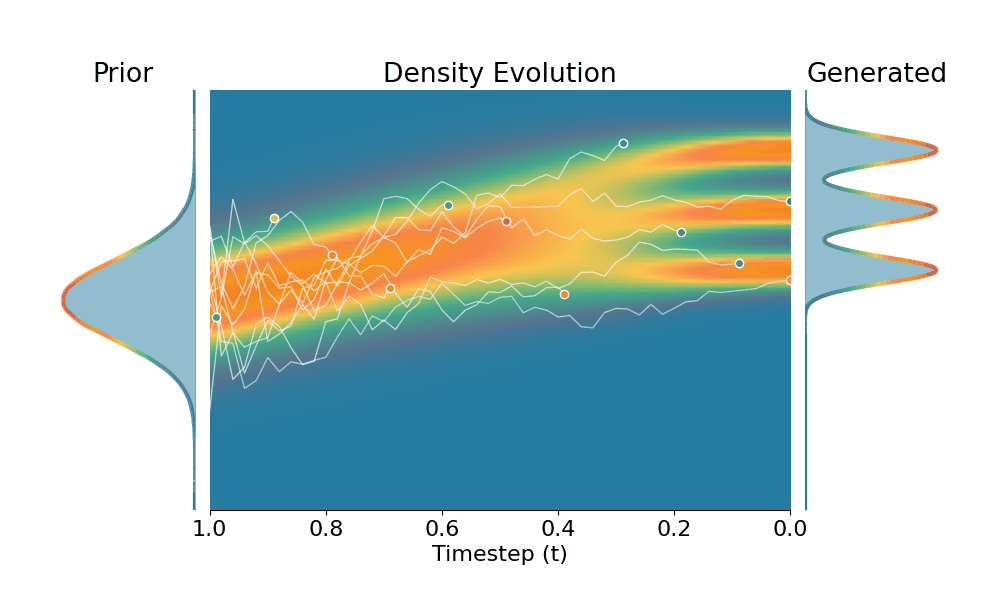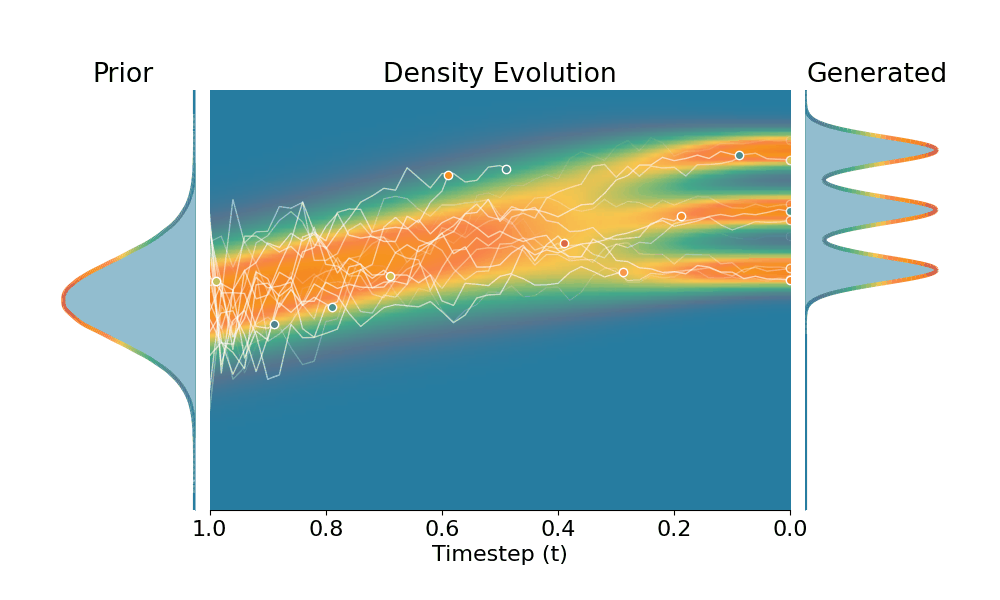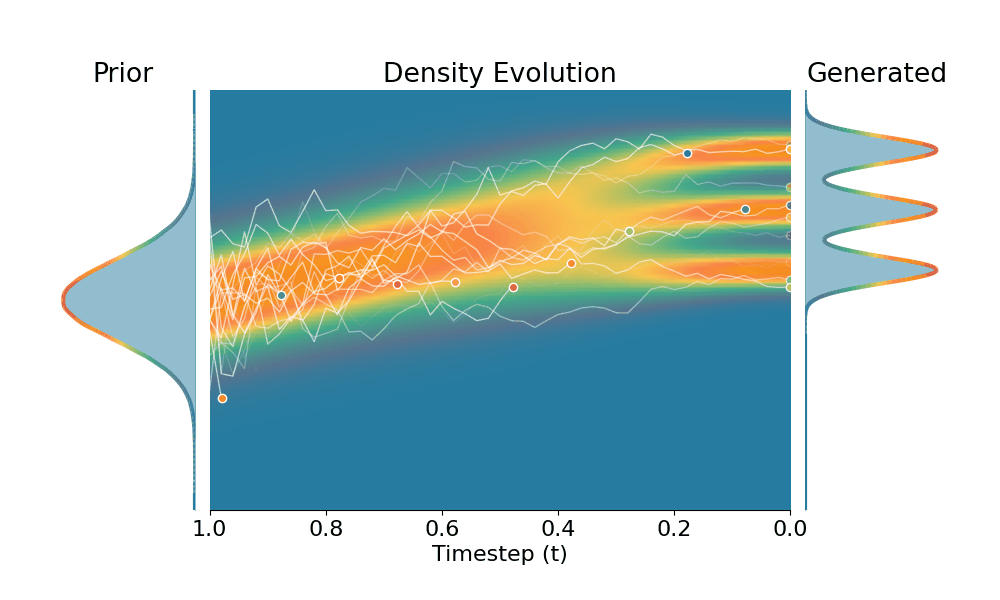
Original (DDPM, class 0)
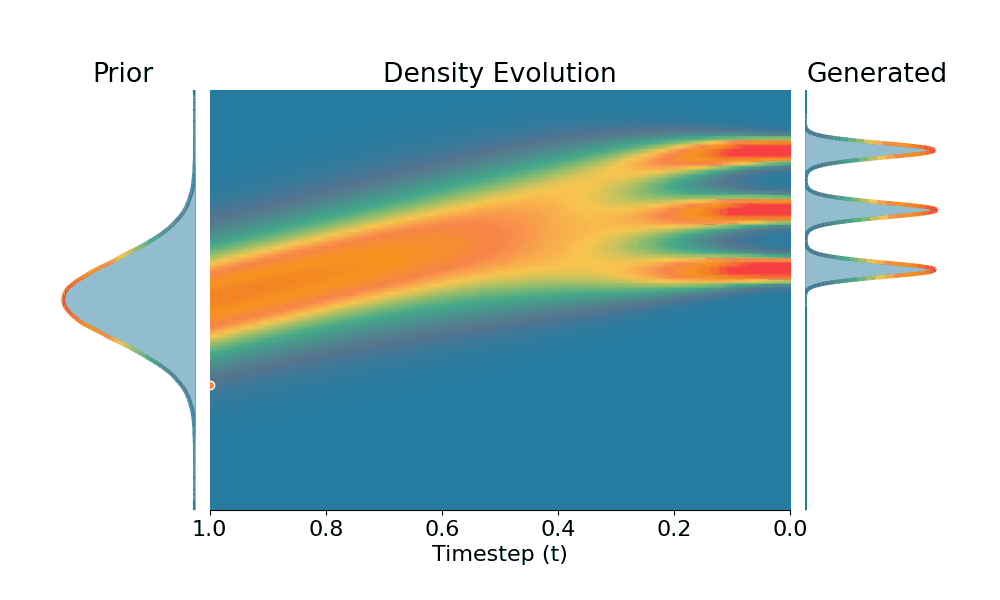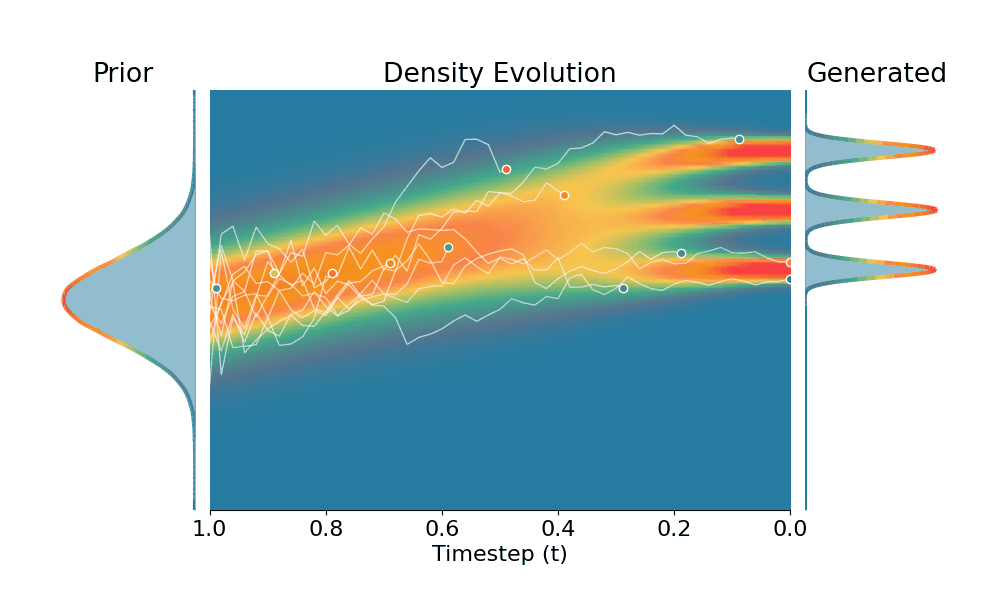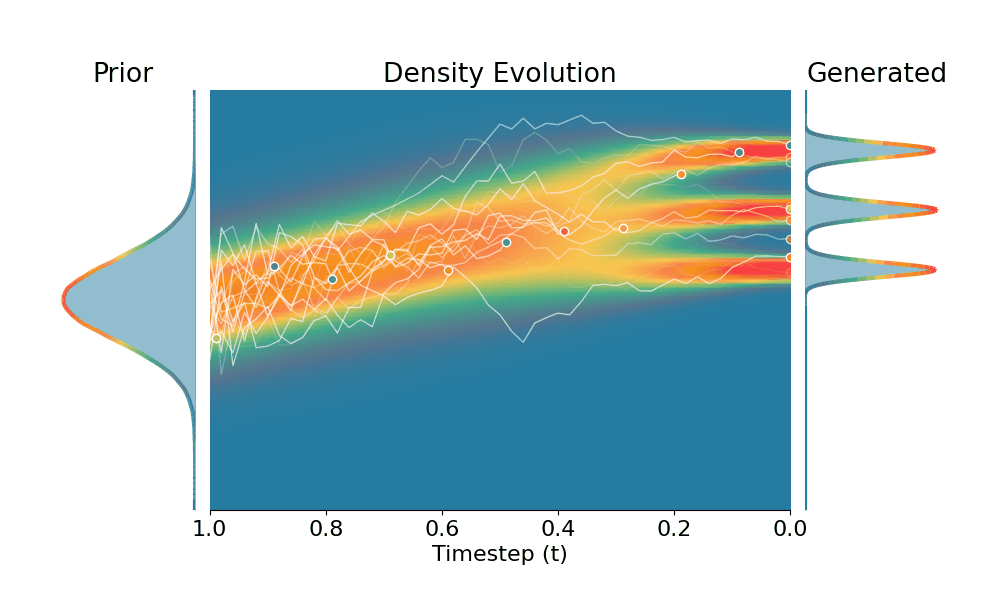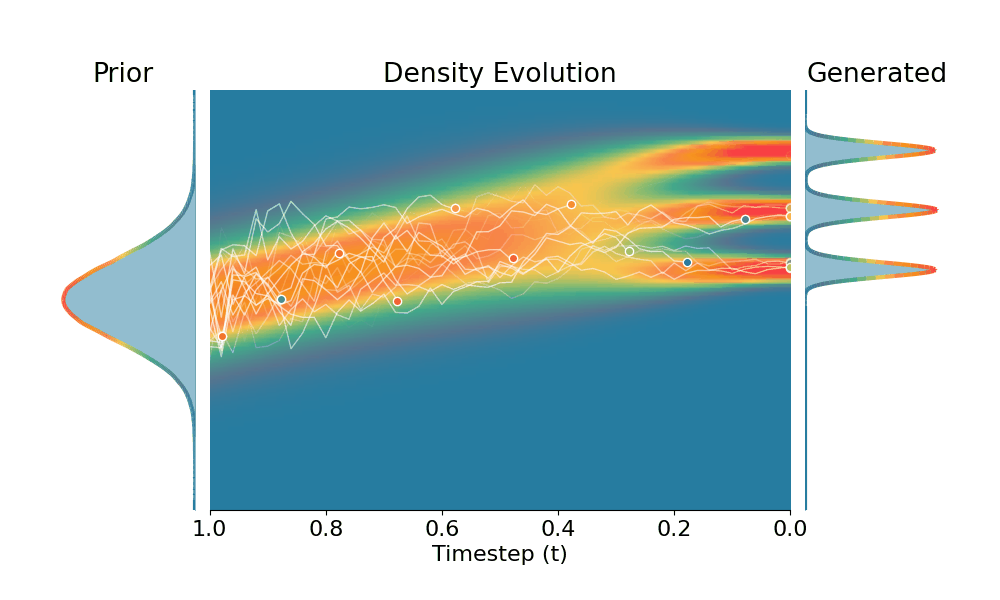
+Temporal Score Rescaling (Ours)
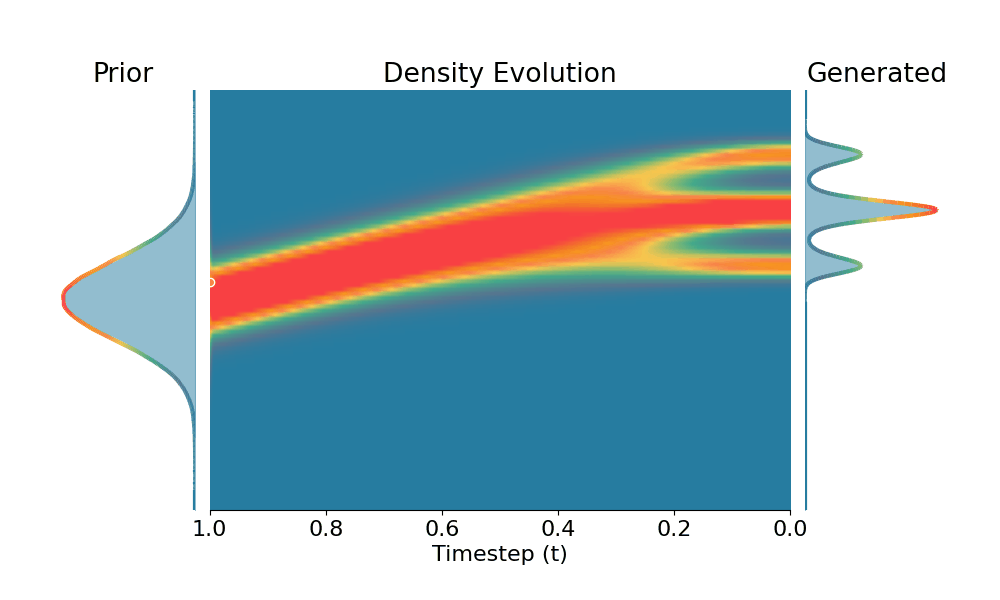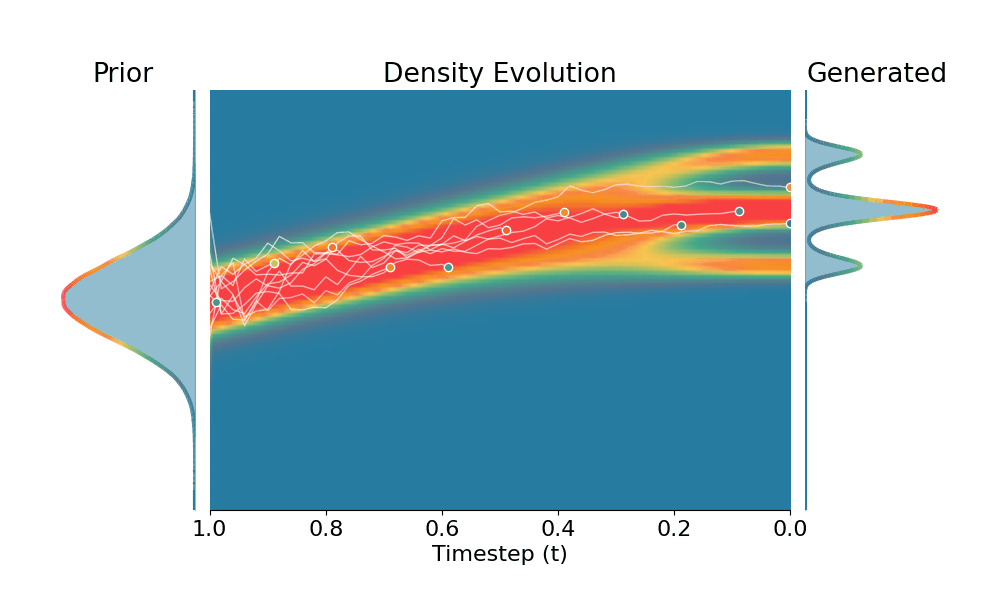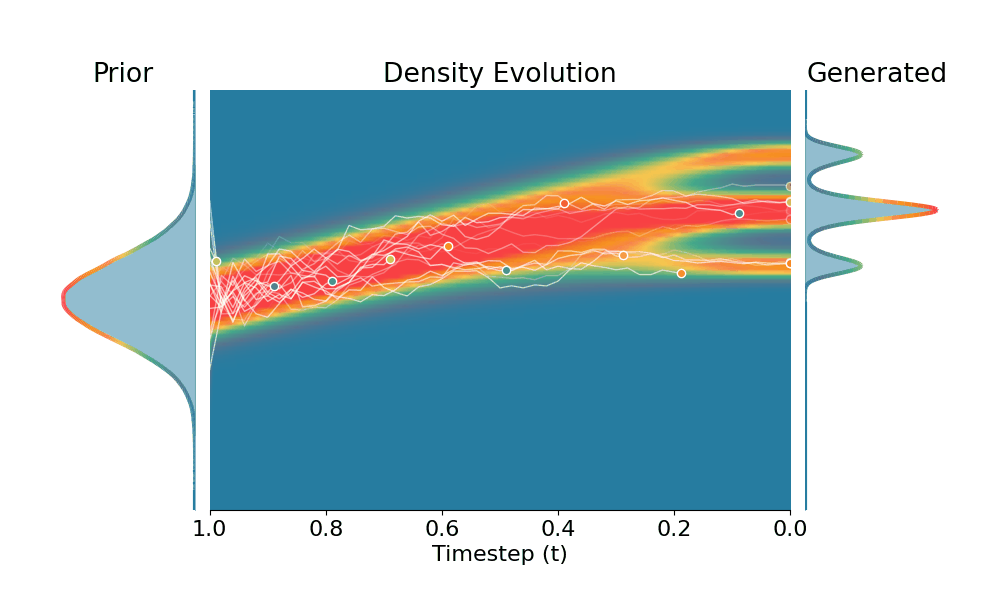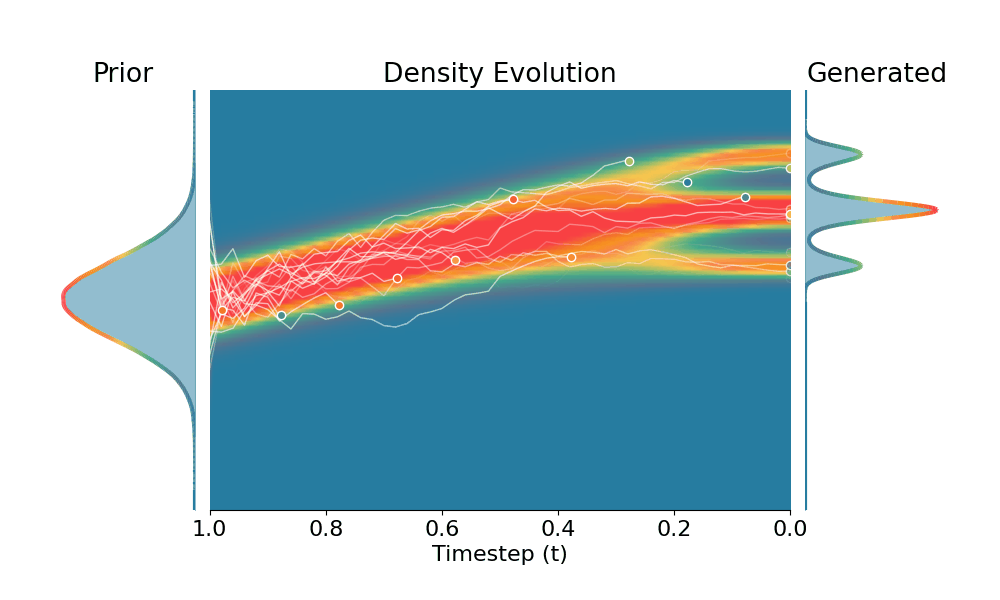
+Constant Noise Scaling
Drag the slider to control $k$ value for TSR and CNS, or the guidance scale for CFG.
The data distribution contains 6 Gaussians with top 3 modes belonging to class 1 and bottom 3 modes to class 2. Showing conditional distribution for class 1.